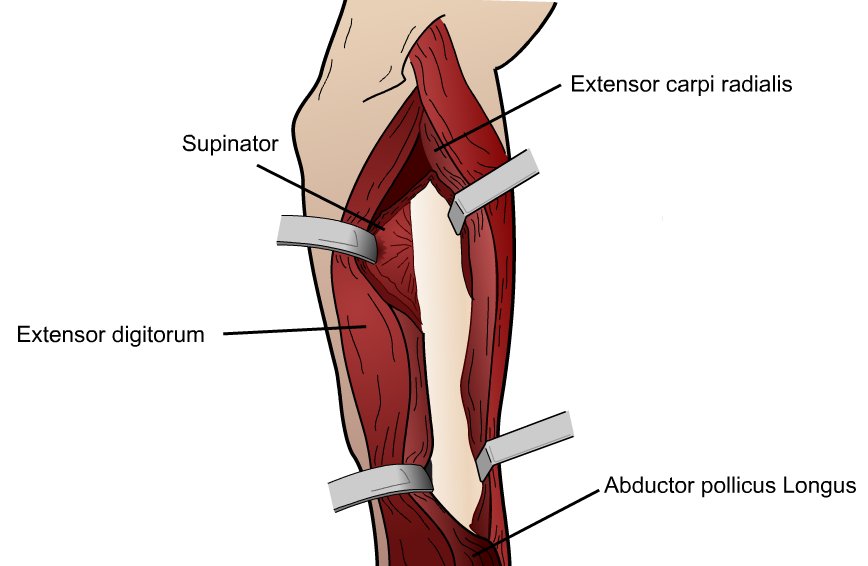
Posteriolateral Approach to the Forearm (Thompsons)
Indication
Access to the posterior radius. Most commonly used for access to proximal 2/3rds although may be extended distally. The thompson's approach allows access for proximal radial-ulnar joint surgery.
Plating of the proximal radius may be achieved through this approach with less risk of mechanical block to prono-supination.
Anatomy
Proximally :
- Internervous plane between extensor digitorum communus (EDC) and extensor carpi-radialis brevis (ECRB)
- EDC is supplied by posterior interosseous nerve, ECRB by radial nerve
Distally :
- Internervous plane between ECRB and abductor policus longus (APL)
- ECRB supplied by radial nerve, APL posterior interosseous n.
Positioning
Supine
Arm
Board
Tourniquet on upper arm (Elevate,
Donít exsanguinate to keep V's engorged).
Forearm in pronation
Skin Incision
A straight line from Lister's tubercle to just anterior to the lateral epicondyle
Superficial dissection
Expose the deep fascia of the forearm and identify the plane between EDC and ECRB
Incise the fascia, and develop the plane between the two muscles
If requiring access to the distal radius curve radially into the interval of ECRB and EPL
Expose and identify supinator
This image is (c) Ben Ollivere and provided for educational purposes only. It may not be reproduced in any form without permission of the author.
Deep dissection
Proximal 2/3rds:
Elevate the supinator from the bone. Care should be taken as the muscle belly contains the post. interosseous nerve
NB. Start distally and work proximally, elevating supinator sub-periosteally.
Watch for post. interosseus Ní in supinator belly & avoid excessive traction.
Semi-supination may help to relieve the tension on the muscle.
Identify and preserve the post, int. nerve leaving the muscle belly 1cm proximal to the inferior edge
Reflect the elevated supinator to protect the nerve
Distal 1/3rd:
Incise the radial border of the APL
Subperiosteally dissect APL off the radius until mobile and reflect ulnawards
If working more distally the EPB may also need to be elevated or reflected
Exposure extension
The approach provides exposure to the whole radius, and may be extended into the dorsal wrist approach distal to Lister's tubercle if required.
Closure
Tack together the muscle planes with tension free sutures to reduce the scaring.
The fascia and skin should be thoroughly repaired.
Post operatively
Post operative management depends on the indication for operation.
It is advisable to rest the arm in a plaster given the extent of muscle stripping associated with this approach at least until the skin heals irrespective of the operation performed.
References
(1) Anatomical methods of approach in operations on the long bones of the extremities. JE Thompson. Ann Surg. Vol 68. 1918. p 309-329.